Van laptop naar de Cloud: AI-model Deployen op Hugging Face Hub & Spaces
/
Van laptop naar de Cloud: AI-model Deployen op Hugging Face Hub & Spaces
AI-modellen blijven over het algemeen vaak hangen in een onderzoeksfase. AI-onderzoekers, data scientists en data engineers denken nog te weinig na over de praktische implementatie van een AI-model.
Gelukkig worden er al maar betere tools ter beschikking gesteld om AI-modellen in de praktijk te gebruiken. HuggingFace bracht jaren geleden al een eerste Transformers library uit, waarmee complexe LLM-modellen, gebaseerd op Transformers konden gebruikt worden. Dit nam heel wat complexiteit weg, en HuggingFace zette zo een standaard voor de AI-wereld.
Main section
Kerngegevens
/
Opgestart in 2016
/
Web-apps, datasets, models
/
Transformers library
/
PyTorch, Tensorflow & JAX
Wat kan je allemaal met Hugging Face doen?
HuggingFace? Wat is dat?
Hugging Face is een open, community-gedreven platform én modelhub voor machine learning waarmee je in één uniforme omgeving AI-modellen kunt ontdekken, delen en hosten. Dankzij de Hub kun je modellen publiceren voor uiteenlopende frameworks, van PyTorch en TensorFlow tot JAX en pure Keras. Je profiteert van versiebeheer en modelinformatie (via zogenaamde Cards) om je werk reproduceerbaar en herbruikbaar te maken. Daarmee fungeert de Hub niet alleen als een soort “GitHub voor AI-modellen”, maar ook als een centrale plek waar je eenvoudig kunt zoeken op tags, prestaties en architectuur.Naast de modelregistry biedt Hugging Face ook Spaces: kant-en-klare, web-apps (meestal gebouwd met Gradio of Streamlit) waarin je jouw modellen direct kunt demonstreren of inzetten als interactieve service. Zonder dat je zelf een cloud-omgeving hoeft op te zetten, kun je in enkele minuten een Space opzetten, de benodigde dependencies definiëren in een `requirements.txt` of `YAML`-frontmatter methodiek, en live testen via een browser-interface.Bovendien ondersteunt het platform ook een dataset-hub: je kunt datasets uploaden (inclusief labeling, splitsen en SQL-queries), die automatisch omgezet worden naar efficiënte Parquet-formaten, en delen met de community.Hierdoor bespaart Hugging Face je de complexiteit van opzet en beheer en kun je je focussen op het ontwerpen en verfijnen van je AI-workflows.
AI-modellen beheren
AI-modellen ontwikkeld door AI engineers worden dezerdagen steeds vaker behandeld als een gebruikelijke Code Asset. Een stukje code dat deel uitmaakt van een groter project. Code verandert vaak, en een AI-model doet dat in het begin van de ontwikkeling ook. De onderzoekers proberen verschillende parameters aan te passen, en bereiken uiteindelijk een werkend resultaat. Als ze dit behandelen zoals andere code, dan wordt dit meestal op een Versiebeheerplatform geplaatst. GitHub is gespecialiseerd in het beheren van code, net zoals SharePoint dat is voor bedrijfsbestanden.
HuggingFace werkt samen met de achterliggende technologie van Git, en bouwt zo een versiebeheersysteem voor AI-modellen uit. Deze modellen kunnen op die manier ook eenvoudig verspreid worden naar andere ontwikkelers en gebruikers. HuggingFace zorgt er ook voor dat een AI Engineer extra informatie toevoegt aan het getrainde model, zodat er transparantie is naar andere gebruikers. De ontwikkelaars voorzien een Model Card met stukjes voorbeeldcode, maar ook statistieken over het AI-model en de kwaliteit ervan. Ze voegen ook een Licentie toe die zegt of het AI-model commercieel gebruikt mag worden, of niet.
HuggingFace CLI tool
HuggingFace heeft een CLI tool ter beschikking gesteld, waardoor taken heel eenvoudiggeautomatiseerd worden.
Zodra je aan account hebt aangemaakt, zorg je voor een authorisatiecode, waarmee de CLI toegang zal krijgen tot jouw account. Je kiest zelf welke rechten er aan deze code aangekoppeld worden. Vervolgens kan je met de cli een Repo of Repository aanmaken, zodat het model kan beheerd worden in het versiebeheersysteem van de Hugging Face Hub.
pip install huggingface_hub
huggingface-cli login
huggingface-cli repo create <your-username>/<repo-name> --type model
Framework onafhankelijk
AI-modellen worden veelal gemaakt met 3 bekende frameworks. Pytorch, Tensorflow of Keras. Er bestaan nog niet heel veel standaarden, behalve ONNX, die framework onafhankelijk zijn.
Keras en Tensorflow zijn gelijkaardig in hun werking, omdat Keras sinds nieuwere versies geïntegreerd is met Tensorflow. Echter gebruikt Keras een `.keras`-bestandsindeling met daardoor een eigen structuur. Deze voldoet niet automatisch aan de structuur die Hugging Face Hub vereist. Hugging Face hanteert een gestandaardiseerde mappenstructuur en metadata (zoals config.json, metadata.json en bestanden die het gewicht van de Neuronen opslaan in HDF5- of PyTorch-formaat) zodat andere tools het model zonder extra aanpassingen kunnen laden. Daarom is een expliciete conversiestap nodig om het model “Hugging Face–ready” te maken.
Conversiestap: van .keras naar uitgepakt SavedModel
Hieronder ziet je een voorbeeld hoe je een pure Keras-bestand omzet naar een uitgepakte SavedModel-structuur die wél aan de HF-vereisten voldoet:

Na uitvoering ontstaat de volgende mappenstructuur onder unpacked_keras/:
unpacked_keras/
├── config.json
├── metadata.json
└── model.weights.h5
Deze structuur kan nu zo op de Hugging Face Hub in een repository geplaatst worden. Keras en HuggingFace laten het ook toe om deze conversie automatisch te doen én te laten pushen naar de Repository:

Als de repository nog niet bestaat, wordt deze automatisch aangemaakt.
Standaard zal het resultaat er zo uit zien:
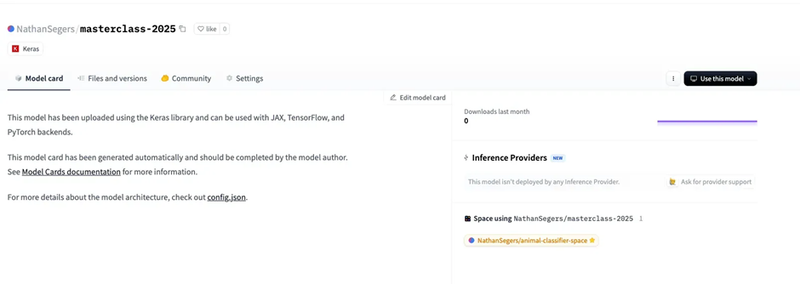
Via het webplatform krijg je nu kant-en-klare code waarmee je jouw AI-model opnieuw kunt downloaden en hergebruiken.
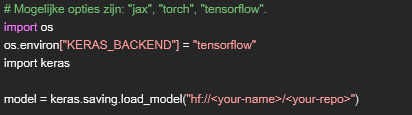
Extra gegevens en versies kunnen altijd toegevoegd worden aan de Repository op dezelfde manier.
AI-model deployment
Omdat AI-ontwikkelaars en -onderzoekers niet altijd de expertise bevatten om een volledig web omgeving te maken waarin het AI-model kan gebruikt, laat HuggingFace het ook toe om getrainde AI-modellen eenvoudig te integreren in eigen gemaakte applicaties. Die applicaties kunnen dan ontwikkeld worden door een gespecialiseerd team.
HuggingFace laat ons echter wel toe om AI-modellen op een eenvoudige manier bruikbaar te stellen in een zogenaamde Space via Gradio of Streamlit. Deze frameworks, gebouwd in Python, zijn gebaseerd op onderliggende Javascript technologieën om de browser omgevingen krachtig en efficiënt op te maken. Zo hoeft een developer geen complexe Javascript frameworks te leren, om een eenvoudig ogende, maar toch responsieve webapplicatie op te maken.
Wat is Gradio?
Gradio is een open-source Python-bibliotheek waarmee je in enkele regels code interactieve webinterfaces rondom je machine-learningmodellen bouwt. Dankzij Gradio leg je het fundament van je applicatie vast volgens het klassieke Input → Processing → Output-patroon, terwijl onder de motorkap automatisch een FastAPI-endpoint wordt gegenereerd. Je profiteert zo van een eenvoudige manier om zowel visuele interfaces als een REST-API beschikbaar te stellen, zonder dat je zelf een webserver of API-framework hoeft in te richten.
Door de naadloze ondersteuning voor Gradio binnen HuggingFace, kan je heel snel aan de slag: zodra je je Gradio code in een Space publiceert, containeriseert het platform automatisch je Python-omgeving en dependencies. Met de gratis versie kun je snel prototype-interfaces debuggen en testen, waarna je eenvoudig publieke demo’s lanceert. Bovendien kun je via de Hugging Face CLI Spaces aanmaken en bijwerken. Dit is perfect voor CI/CD-workflows of volledige automatisering, zonder dat je handmatig instellingen in de Hub hoeft door te voeren.
De manier om een Space op te zetten is gelijkaardig aan dat van een Repository. Alleen zullen we nu inhoudelijk een verschil krijgen. De file structuur bevat minstens een `app.py`en een `requirements.txt` er kan ook nog een `README.md` file bij om de Space pagina op HuggingFace van informatie te voorzien. De requirements zijn nodig om alle extra Python packages te installeren.
ai-model-space/
├── app.py
├── README.md
└── requirements.txt
In onze code voor Gradio zullen we zien dat HuggingFace er voor kiest om binnen de Gradio Space telkens de laatste versie van het AI model te downloaden. Dat zorgt ervoor dat de interface en het AI-model gescheiden van elkaar kunnen ontwikkeld worden, en hoeven er geen gezamenlijke updates te komen. Het zorgt er wel voor dat er een kleine extra vertraging opduikt bij het opstarten van de Gradio Space, afhankelijk van de grootte van het AI-model.

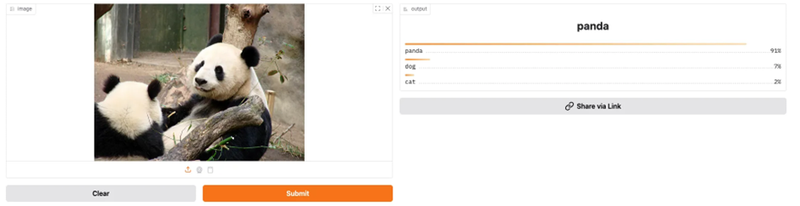
Het resultaat van deze Gradio applicatie zie je in de Space zodra je deze opstart. De applicatie classificeert afbeeldingen van Pandas, Katten en Honden. Hieronder een voorbeeld.
Datasetbeheer op Hugging Face Hub
Hugging Face biedt niet alleen een modelhub, maar ook een volwaardig platform om datasets te creëren, te beheren en te delen. Net als bij modellen wordt elke dataset opgeslagen in een Git-repository, waarbij grotere bestanden automatisch via Git LFS verwerkt worden. Dit garandeert volledige versiecontrole en samenwerking binnen teams, zonder dat je je zorgen hoeft te maken over complexe cloud systemen of ingewikkelde data-pipelines.
Na het uploaden van je data, bijvoorbeeld afbeeldingen voor een classificatie model, kan je ze direct in de Hub van labels voorzien, in train-, validatie- en test-subsets splitsen en zelfs doorzoeken met eenvoudige SQL-achtige queries. Achter de schermen converteert Hugging Face de bestanden automatisch naar het `Parquet`-formaat, wat niet alleen opslagruimte bespaart, maar ook snelle, kolomgeoriënteerde queries en analyses mogelijk maakt. Zo heb je alle tools binnen handbereik om je dataset eenvoudig reproduceerbaar en schaalbaar in te zetten, alsook te voorzien van transparantie
Bottom section
Transparantie
AI-model deployments zijn niet langer een geheim, maar zijn wel heel belangrijk om omzet te kunnen maken. Meer nog, door AI-modellen te gebruiken, kunnen ze verbeterd worden met nieuwe inzichten.
Een belangrijk punt is en blijft transparantie. Aan een gebruiker meedelen dat een AI-model gebruikt wordt, en kunnen verklaren welke beslissing er gemaakt werd, blijft cruciaal. Ook daar speelt HuggingFace een grote rol, door de transparantie van de model informatie en de dataset gegevens.
Wil je meer weten over transparantie van AI-modellen? Hou dan zeker deze blog in de gaten, en aarzel niet om ons te contacteren voor meer informatie!

